Embark on an educational journey with our comprehensive plant cell organelles and structures worksheet answers. This guide unveils the intricacies of plant cell biology, empowering you with a profound understanding of these fundamental components and their indispensable roles in plant life.
Our meticulously crafted content delves into the diverse types of organelles and structures found within plant cells, exploring their specialized functions and strategic locations. Discover how these cellular marvels orchestrate a symphony of processes, ensuring the optimal growth, development, and survival of plants.
Plant Cell Organelles and Structures
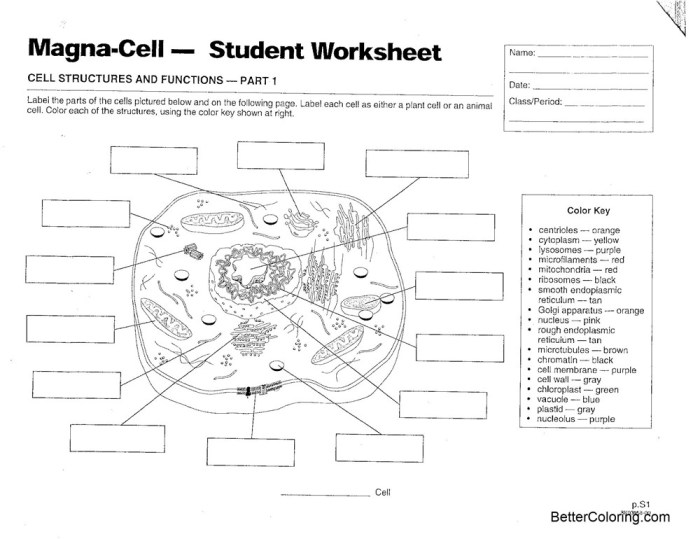
Plant cells are complex structures that contain a variety of organelles and structures that perform specific functions essential for the cell’s survival and growth. These organelles and structures include the nucleus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuoles, and cell wall.
Types of Plant Cell Organelles and Structures, Plant cell organelles and structures worksheet answers
- Nucleus:The nucleus is the control center of the cell and contains the cell’s genetic material, DNA.
- Chloroplasts:Chloroplasts are green organelles that contain chlorophyll and are responsible for photosynthesis.
- Mitochondria:Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell and produce energy through cellular respiration.
- Ribosomes:Ribosomes are small organelles that are responsible for protein synthesis.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum:The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that is responsible for transporting materials within the cell.
- Golgi Apparatus:The Golgi apparatus is a stack of membranes that is responsible for modifying and packaging proteins.
- Vacuoles:Vacuoles are large, fluid-filled organelles that are responsible for storing water and nutrients.
- Cell Wall:The cell wall is a rigid structure that surrounds the cell and provides support and protection.
Functions of Plant Cell Organelles and Structures
Each plant cell organelle and structure has a specific function that contributes to the overall functioning of the cell. The nucleus controls the cell’s activities and contains the cell’s genetic material. Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
Mitochondria produce energy through cellular respiration, the process by which cells break down glucose to produce ATP. Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis, the process by which cells create new proteins. The endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for transporting materials within the cell.
The Golgi apparatus is responsible for modifying and packaging proteins. Vacuoles are responsible for storing water and nutrients. The cell wall provides support and protection for the cell.
The different plant cell organelles and structures work together to maintain cellular homeostasis. For example, the nucleus controls the cell’s activities and coordinates the activities of the other organelles. The endoplasmic reticulum transports materials within the cell, including the proteins that are produced by the ribosomes.
The Golgi apparatus modifies and packages proteins, which are then transported to their final destination by the endoplasmic reticulum. Vacuoles store water and nutrients, which are essential for the cell’s survival. The cell wall provides support and protection for the cell, which is essential for the cell’s ability to withstand changes in its environment.
Importance of Plant Cell Organelles and Structures
Plant cell organelles and structures are essential for the survival and growth of plants. Without these organelles and structures, plants would not be able to perform photosynthesis, produce energy, or store water and nutrients. This would ultimately lead to the death of the plant.
Disruptions to the normal functioning of plant cell organelles and structures can have a variety of consequences. For example, damage to the nucleus can lead to cell death. Damage to the chloroplasts can lead to a decrease in photosynthesis, which can lead to a decrease in energy production.
Damage to the mitochondria can lead to a decrease in cellular respiration, which can also lead to a decrease in energy production. Damage to the endoplasmic reticulum can lead to a decrease in protein synthesis, which can lead to a variety of problems, including cell death.
Damage to the Golgi apparatus can lead to a decrease in the modification and packaging of proteins, which can also lead to a variety of problems, including cell death. Damage to the vacuoles can lead to a decrease in the storage of water and nutrients, which can also lead to cell death.
Damage to the cell wall can lead to a decrease in support and protection for the cell, which can also lead to cell death.
Plant Cell Organelles and Structures in Context
Plant cell organelles and structures are similar to those found in other types of cells, such as animal cells. However, there are some unique features of plant cell organelles and structures that enable plants to perform photosynthesis and other specialized functions.
For example, plant cells have chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis. Plant cells also have a cell wall, which provides support and protection for the cell. These unique features enable plants to perform the essential functions that are necessary for their survival and growth.
Clarifying Questions: Plant Cell Organelles And Structures Worksheet Answers
What are the primary functions of chloroplasts?
Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy-rich molecules, providing the foundation for plant growth and sustenance.
How do mitochondria contribute to plant cell metabolism?
Mitochondria serve as the powerhouses of plant cells, generating energy through cellular respiration, a vital process for maintaining cellular function and growth.
What is the significance of the cell wall in plant cells?
The cell wall, a rigid structure surrounding the cell membrane, provides structural support, protection, and maintains the shape of plant cells, enabling them to withstand external pressures.