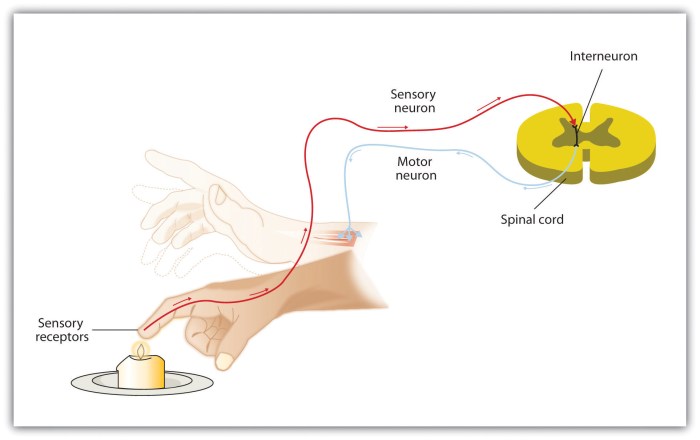
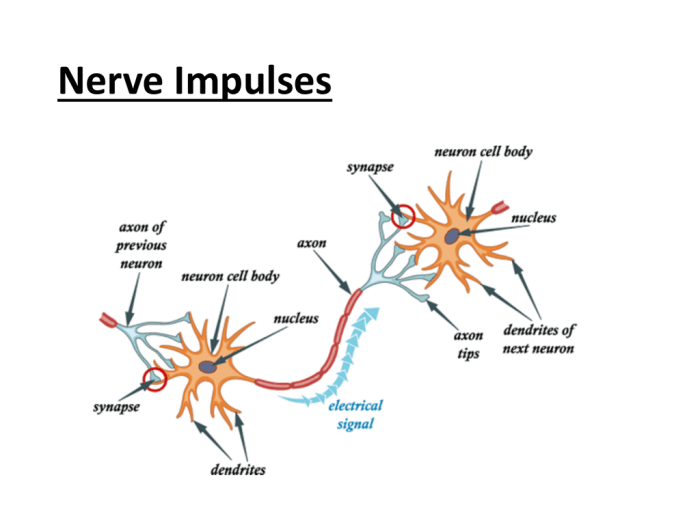
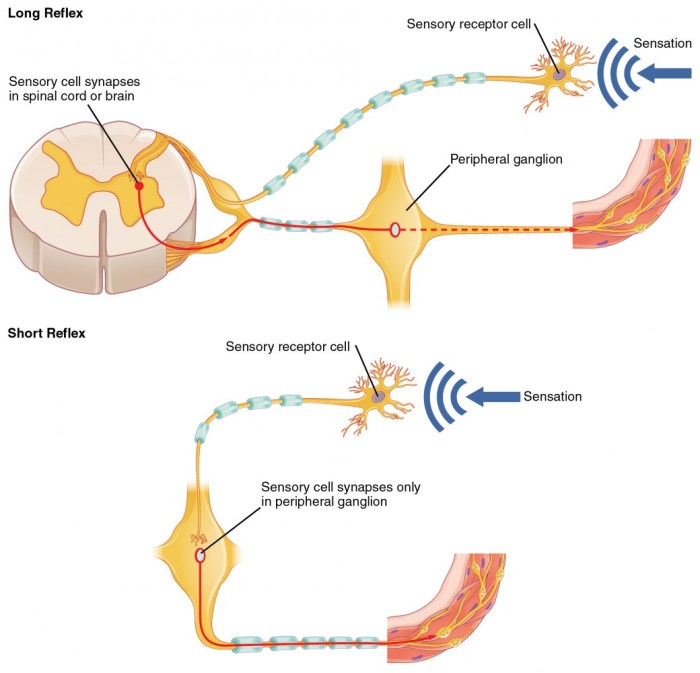
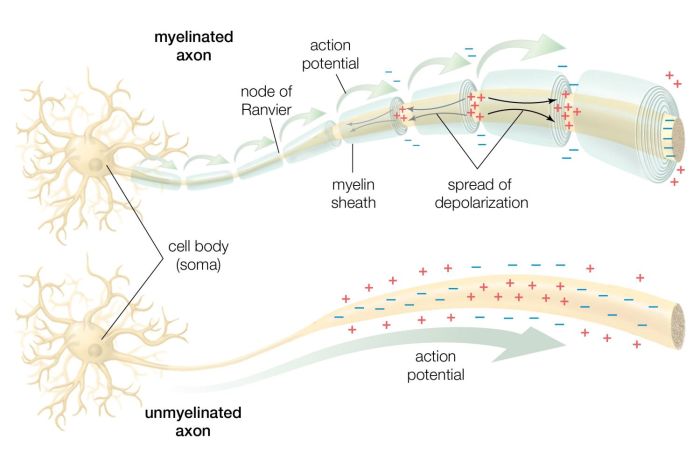
Select the true statement regarding first-order neurons. – First-order neurons, the gatekeepers of sensory information, play a crucial role in our perception of the world. They are the primary recipients of sensory stimuli, transforming them into electrical signals that can be processed by the brain. Understanding the properties and functions of first-order neurons is essential for unraveling the complexities of sensory processing and perception.
These specialized neurons possess unique characteristics that enable them to encode and transmit sensory information with remarkable precision. Their receptive fields, response properties, and synaptic plasticity contribute to their ability to extract meaningful patterns from the vast array of sensory stimuli we encounter.
First-Order Neurons
First-order neurons, also known as primary sensory neurons, are specialized nerve cells that receive sensory information from the environment and transmit it to the central nervous system (CNS). They play a crucial role in sensory perception and the formation of our understanding of the world around us.
Structure and Function of First-Order Neurons
First-order neurons have a unique structure that enables them to receive and transmit sensory information. They consist of three main parts:
- Receptor:The receptor is a specialized protein located on the dendrite of the neuron. It is responsible for detecting specific stimuli, such as light, sound, or touch.
- Cell body:The cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles necessary for the neuron’s survival and function.
- Axon:The axon is a long, thin fiber that transmits the electrical signals generated by the neuron to the CNS.
When a stimulus is detected by the receptor, it triggers a series of electrical and chemical changes in the neuron. These changes result in the generation of an action potential, which is an electrical impulse that travels along the axon towards the CNS.
Properties of First-Order Neurons
First-order neurons have several unique properties that enable them to perform their specialized function:
Receptive Fields
Each first-order neuron has a specific receptive field, which is the area of the sensory environment from which it receives input. The receptive field is determined by the location and sensitivity of the neuron’s receptor.
Response Properties
First-order neurons exhibit characteristic response properties, including:
- Firing rate:The firing rate of a neuron is the number of action potentials it generates per second. The firing rate is typically proportional to the intensity of the stimulus.
- Adaptation:First-order neurons adapt to continuous stimuli over time, reducing their firing rate. This adaptation allows the neuron to respond more effectively to changes in the sensory environment.
Encoding Sensory Information
First-order neurons encode sensory information in the pattern of action potentials they generate. The frequency and timing of the action potentials convey information about the intensity, location, and quality of the stimulus.
Signal Processing in First-Order Neurons, Select the true statement regarding first-order neurons.
The generation and transmission of signals in first-order neurons involve several key processes:
Ion Channels
Ion channels are proteins located in the neuron’s membrane that allow the passage of specific ions, such as sodium and potassium. The opening and closing of these channels control the electrical potential of the neuron and the generation of action potentials.
Neurotransmitter Release
When an action potential reaches the end of the axon, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that transmit the signal to other neurons across the synaptic cleft.
Synaptic Plasticity
Synaptic plasticity refers to changes in the strength of the connections between neurons. In first-order neurons, synaptic plasticity plays a role in learning and memory by adjusting the sensitivity of the neuron to specific stimuli.
First-Order Neurons in Sensory Systems
First-order neurons are essential components of all sensory systems, including:
- Vision:First-order neurons in the retina receive light stimuli and transmit them to the visual cortex in the brain.
- Hearing:First-order neurons in the cochlea receive sound waves and transmit them to the auditory cortex in the brain.
- Touch:First-order neurons in the skin receive tactile stimuli and transmit them to the somatosensory cortex in the brain.
- Taste:First-order neurons in the taste buds receive chemical stimuli and transmit them to the gustatory cortex in the brain.
- Smell:First-order neurons in the olfactory epithelium receive odor molecules and transmit them to the olfactory bulb in the brain.
First-order neurons play a crucial role in sensory integration, the process by which the brain combines information from different sensory modalities to create a coherent perception of the environment.
Applications of First-Order Neurons in Neuroscience
First-order neurons are valuable tools for studying sensory processing and developing therapies for sensory disorders:
- Sensory processing:First-order neurons can be recorded from and manipulated to study the neural mechanisms underlying sensory perception.
- Sensory disorders:Understanding the function of first-order neurons can lead to the development of new treatments for sensory disorders, such as deafness and blindness.
- Neuroprosthetics:First-order neurons can be used to develop neuroprosthetics, devices that can restore or enhance sensory function in individuals with sensory loss.
Quick FAQs: Select The True Statement Regarding First-order Neurons.
What are the key properties of first-order neurons?
First-order neurons are characterized by their receptive fields, response properties (firing rates and adaptation), and ability to encode sensory information.
How do first-order neurons contribute to sensory perception?
First-order neurons play a crucial role in converting sensory stimuli into electrical signals that can be processed by the brain, forming the basis for our perception of the world.
What are the applications of first-order neurons in neuroscience?
First-order neurons are used to study sensory processing, develop therapies for sensory disorders, and explore potential applications in neuroprosthetics.