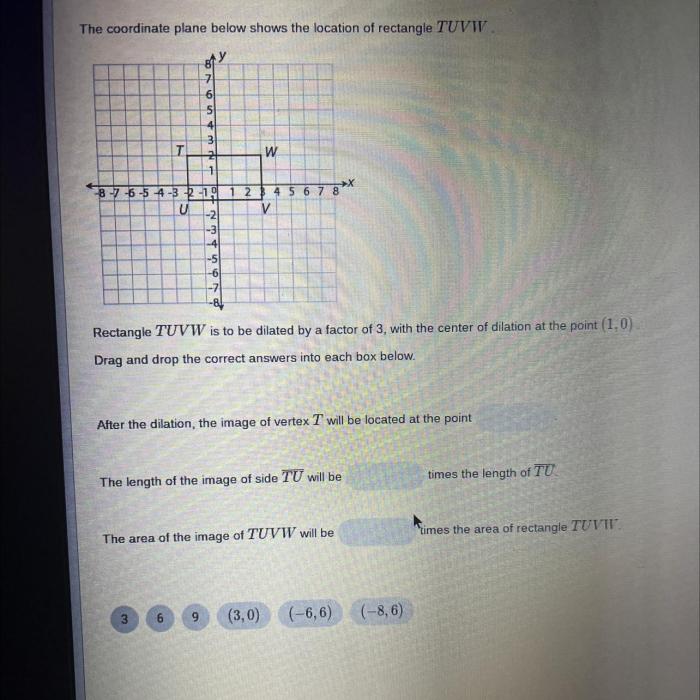
Rectangle tuvw is on a coordinate plane at t – Rectangle TUVW, situated on a coordinate plane at time t, presents a captivating subject for exploration. Its properties, coordinates, and transformations offer insights into the fundamental principles of geometry and provide a foundation for understanding its diverse applications across various fields.
Delving into the intricacies of rectangle TUVW, we unravel the relationships between its opposite sides and diagonals, identify the coordinates of its vertices, and explore techniques for calculating its midpoint and area. Furthermore, we delve into transformations, elucidating how to translate, rotate, and reflect the rectangle using vector notation and geometric principles.
Rectangular Properties
A rectangle is a quadrilateral with four right angles and four sides of equal length. Rectangle TUVW has the following properties:
- Opposite sides are parallel and of equal length.
- Adjacent sides are perpendicular to each other.
- The diagonals of the rectangle bisect each other.
Relationship Between Opposite Sides
The opposite sides of a rectangle are parallel and of equal length. This means that the distance between any two opposite sides is the same. For example, in rectangle TUVW, the distance between side TU and side VW is the same as the distance between side TV and side UW.
Relationship Between Diagonals
The diagonals of a rectangle bisect each other. This means that the diagonals intersect at a point that is the midpoint of both diagonals. For example, in rectangle TUVW, the diagonals TU and VW intersect at point O, which is the midpoint of both diagonals.
Rectangle Coordinates
The coordinates of the vertices of rectangle TUVW are as follows:
- T(x1, y1)
- U(x2, y1)
- V(x2, y2)
- W(x1, y2)
The midpoint of a side of a rectangle is the average of the coordinates of the endpoints of the side. For example, the midpoint of side TU is ((x1+x2)/2, (y1+y2)/2).
The area of a rectangle is the product of its length and width. The length of a rectangle is the distance between any two opposite sides. The width of a rectangle is the distance between any two adjacent sides. For example, the area of rectangle TUVW is (x2-x1)*(y2-y1).
Transformations: Rectangle Tuvw Is On A Coordinate Plane At T
Rectangles can be transformed using translation, rotation, and reflection.
Translation
Translation is the movement of a figure from one point to another without changing its size or shape. To translate rectangle TUVW by vector (a, b), each vertex of the rectangle is moved a units to the right and b units up.
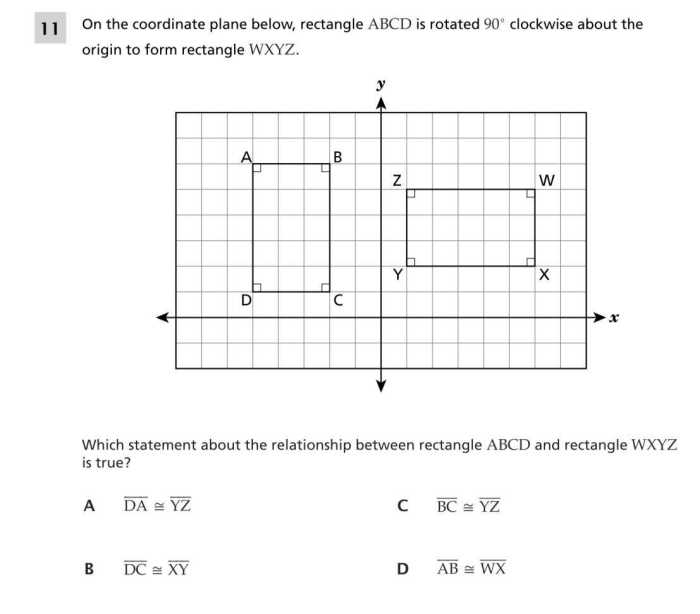
Rotation, Rectangle tuvw is on a coordinate plane at t
Rotation is the turning of a figure around a fixed point. To rotate rectangle TUVW around point (x, y) by angle θ, each vertex of the rectangle is rotated θ degrees around the point (x, y).
Reflection
Reflection is the flipping of a figure over a line. To reflect rectangle TUVW over the line y = x, each vertex of the rectangle is reflected over the line y = x.
Applications
Rectangles are used in a variety of fields, including geometry, physics, and engineering. In geometry, rectangles are used to study the properties of two-dimensional shapes. In physics, rectangles are used to calculate the area and volume of objects. In engineering, rectangles are used to design buildings and other structures.
Rectangles are also used in computer graphics and design. In computer graphics, rectangles are used to create shapes and textures. In design, rectangles are used to create layouts and other visual elements.
FAQ Resource
What are the key properties of rectangle TUVW?
Rectangle TUVW exhibits several key properties, including equal opposite sides, congruent diagonals that bisect each other, and right angles at each vertex.
How do you find the midpoint of a side of rectangle TUVW?
To find the midpoint of a side of rectangle TUVW, average the coordinates of its endpoints using the midpoint formula: Midpoint = ((x1 + x2) / 2, (y1 + y2) / 2).
What are the steps involved in translating rectangle TUVW using vector notation?
Translating rectangle TUVW using vector notation involves adding the translation vector to the coordinates of each vertex: (x’, y’) = (x + h, y + k), where (h, k) is the translation vector.