Identify the highlighted structure. heart – The heart, a vital organ, plays a central role in the circulatory system, pumping oxygenated blood throughout the body. Its intricate structure and function are essential for sustaining life.
The heart’s four chambers, valves, and electrical system work in harmony to regulate blood flow, maintain heart rate, and respond to the body’s demands. Understanding the anatomy and physiology of the heart is crucial for comprehending its role in overall health and well-being.
1. Structure and Anatomy of the Heart

The heart is a muscular organ located in the thoracic cavity, between the lungs. It is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body, providing oxygen and nutrients to the cells and removing waste products.
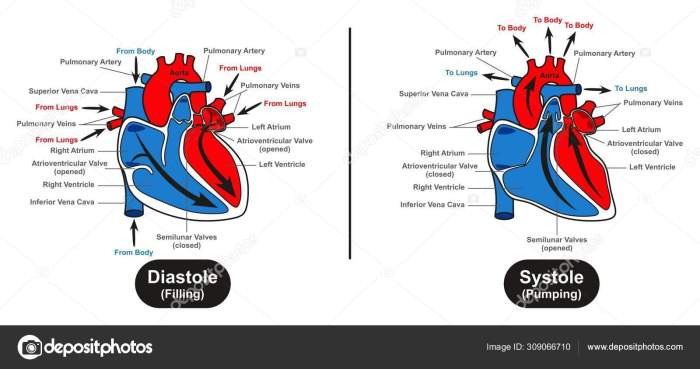
Four Chambers of the Heart
- Right atrium:Receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the superior and inferior vena cava.
- Right ventricle:Pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery.
- Left atrium:Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins.
- Left ventricle:Pumps oxygenated blood to the body via the aorta.
Heart Valves
The heart valves ensure that blood flows in the correct direction through the heart:
- Tricuspid valve:Between the right atrium and right ventricle.
- Pulmonary valve:Between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery.
- Mitral valve (bicuspid valve):Between the left atrium and left ventricle.
- Aortic valve:Between the left ventricle and aorta.
2. Blood Flow through the Heart
Blood flows through the heart in a specific pathway:
- Vena cava:Deoxygenated blood from the body enters the heart through the superior and inferior vena cava.
- Right atrium:Blood enters the right atrium.
- Tricuspid valve:Blood flows through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle.
- Pulmonary valve:Blood flows through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery.
- Lungs:Blood is oxygenated in the lungs.
- Pulmonary veins:Oxygenated blood returns to the heart via the pulmonary veins.
- Left atrium:Blood enters the left atrium.
- Mitral valve:Blood flows through the mitral valve into the left ventricle.
- Aortic valve:Blood flows through the aortic valve into the aorta.
- Body:Oxygenated blood is pumped throughout the body via the aorta.
Regulation of Heart Rate
The heart rate is regulated by the sinoatrial node (SA node) and the atrioventricular node (AV node):
- SA node:Generates electrical impulses that initiate heart contractions.
- AV node:Delays the electrical impulses, allowing the atria to fill with blood before the ventricles contract.
3. Electrical Activity of the Heart

The heart’s electrical activity is essential for coordinating heart contractions:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG):Records the electrical activity of the heart.
- P wave:Represents the electrical impulse spreading through the atria.
- QRS complex:Represents the electrical impulse spreading through the ventricles.
- T wave:Represents the ventricles repolarizing after contraction.
Heart Rhythm Disorders, Identify the highlighted structure. heart
Abnormal electrical activity can lead to heart rhythm disorders:
- Bradycardia:Slow heart rate.
- Tachycardia:Fast heart rate.
- Arrhythmias:Irregular heartbeats.
4. Blood Vessels and Circulation

Blood vessels are essential for transporting blood throughout the body:
Types of Blood Vessels
- Arteries:Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart.
- Veins:Carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
- Capillaries:Tiny vessels where oxygen and nutrients are exchanged with cells.
Circulatory System
The circulatory system transports oxygen and nutrients to the cells and removes waste products:
- Systemic circulation:Transports blood to and from the body’s organs and tissues.
- Pulmonary circulation:Transports blood to and from the lungs for oxygenation.
5. Cardiac Cycle
The cardiac cycle refers to the sequence of events that occur during each heartbeat:
Events of the Cardiac Cycle
- Systole:Ventricles contract, pumping blood out of the heart.
- Diastole:Ventricles relax, filling with blood.
Cardiac Cycle and Heart Rate
The cardiac cycle is related to heart rate:
- Faster heart rate:Shorter cardiac cycle.
- Slower heart rate:Longer cardiac cycle.
Factors Affecting the Cardiac Cycle
Various factors can influence the cardiac cycle:
- Sympathetic nervous system:Increases heart rate and contractility.
- Parasympathetic nervous system:Decreases heart rate and contractility.
- Hormones (e.g., adrenaline):Can increase or decrease heart rate.
FAQ Overview: Identify The Highlighted Structure. Heart
What are the four chambers of the heart?
The four chambers of the heart are the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle.
What is the function of the heart valves?
The heart valves prevent blood from flowing backward in the heart and ensure proper blood flow through the chambers.
What is the role of the sinoatrial node?
The sinoatrial node is the natural pacemaker of the heart, initiating the electrical impulses that trigger heart contractions.