As the contraction of the heart crossword takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with precision and depth, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. Delving into the physiological processes that govern the rhythmic beating of the heart, we embark on a journey that unravels the intricate mechanisms that sustain life itself.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Cardiac Contraction: Physiological Overview
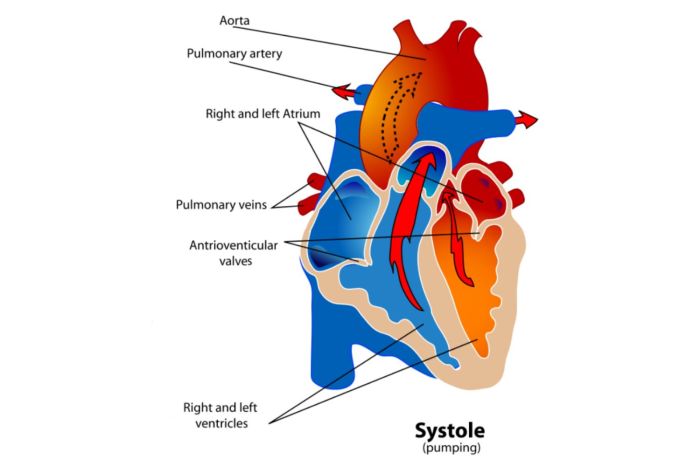
Cardiac contraction is the rhythmic pumping action of the heart, which propels blood throughout the body. It involves a complex interplay of electrical and mechanical events that are tightly coordinated to ensure efficient and synchronized heart function.
Sinoatrial Node (SA Node) and Atrioventricular Node (AV Node)
The SA node, located in the right atrium, is the primary pacemaker of the heart. It generates electrical impulses that initiate the contraction of the atria. These impulses travel to the AV node, which delays the electrical signal slightly before transmitting it to the ventricles.
This delay allows the atria to fill completely before ventricular contraction.
Calcium Ion Movement
Calcium ions play a crucial role in triggering cardiac contraction. During the action potential, an influx of calcium ions into the cardiomyocytes (heart muscle cells) triggers the release of more calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, an intracellular calcium store.
This increased intracellular calcium concentration binds to troponin C, which initiates a conformational change in the troponin complex, allowing actin and myosin filaments to interact and generate force.
Phases of Cardiac Contraction
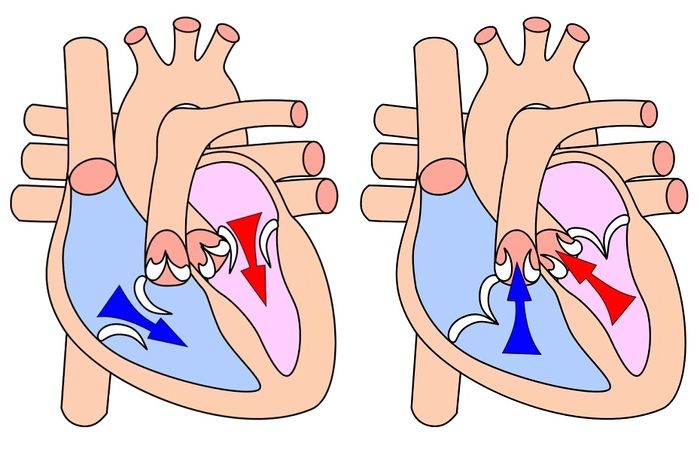
The cardiac contraction cycle can be divided into distinct phases:
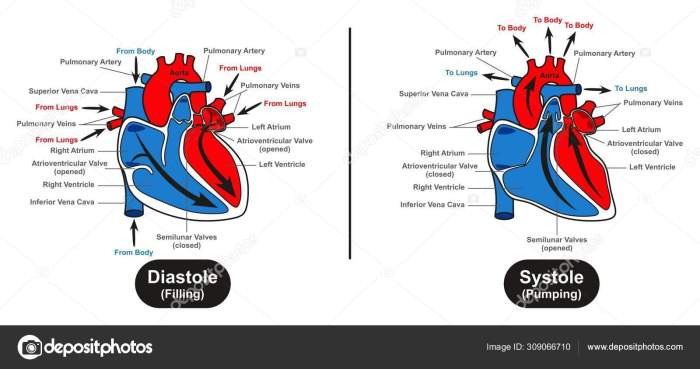
- Diastole:The relaxation phase, during which the heart fills with blood.
- Systole:The contraction phase, during which the heart pumps blood out.
Electrical and Mechanical Events, Contraction of the heart crossword
During diastole, the ventricles are relaxed and filling with blood. The electrical impulse from the SA node reaches the ventricles, triggering ventricular depolarization. This depolarization wave travels through the ventricular myocardium, causing contraction and ejection of blood from the ventricles.
As the ventricles contract, the pressure within them increases, closing the atrioventricular valves and preventing backflow of blood into the atria. The aortic and pulmonary valves open, allowing blood to flow out of the heart into the aorta and pulmonary artery.
At the end of systole, ventricular repolarization occurs, restoring the resting membrane potential and preparing the heart for the next contraction cycle.
Regulation of Cardiac Contraction
The force and rate of cardiac contraction are regulated by various mechanisms:
Autonomic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system increases heart rate and contractility, while the parasympathetic nervous system decreases them.
Hormones
Hormones such as epinephrine and norepinephrine stimulate the heart, increasing its rate and contractility.
Ion Concentrations
Changes in ion concentrations, such as increased calcium or decreased potassium, can affect cardiac contractility.
These regulatory mechanisms work together to ensure that the heart can adapt to changing demands, such as exercise or stress.
Clinical Significance of Cardiac Contraction Abnormalities
Abnormalities in cardiac contraction can have significant clinical implications:
Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias are abnormal heart rhythms that can result from disturbances in the electrical conduction system of the heart.
Heart Failure
Heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. It can result from impaired cardiac contraction.
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle that can affect its ability to contract effectively.
These abnormalities can manifest as symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Diagnosis involves electrocardiography, echocardiography, and other tests. Treatment approaches include medications, lifestyle modifications, and in severe cases, surgical interventions.
Questions and Answers: Contraction Of The Heart Crossword
What is the role of the sinoatrial node in cardiac contraction?
The sinoatrial node (SA node) acts as the natural pacemaker of the heart, initiating the electrical impulses that trigger the contraction sequence.
How does calcium ion movement contribute to cardiac contraction?
The influx of calcium ions into cardiac cells plays a crucial role in triggering the release of stored calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which ultimately leads to muscle contraction.
What are the common causes of cardiac contraction abnormalities?
Cardiac contraction abnormalities can arise from various factors, including coronary artery disease, heart valve disorders, and electrical conduction system defects.
