Embark on an illuminating journey through the French and Indian War Brainpop, where history unfolds in vivid detail. This meticulously crafted exploration delves into the complexities of a pivotal conflict that shaped the destiny of North America.
From the clash of European empires to the resilience of Native American tribes, the French and Indian War left an enduring mark on the continent’s landscape and its people.
Historical Context: French And Indian War Brainpop

The French and Indian War, also known as the Seven Years’ War, was a global conflict that took place between 1754 and 1763. It was the first major war in which the European powers fought on a global scale, with battles taking place in North America, Europe, Africa, and India.
The war’s origins can be traced to the rivalry between France and Great Britain for control of North America. Both countries had established colonies in the New World, and they were competing for territory and resources. The French were allied with several Native American tribes, while the British were allied with the Iroquois Confederacy.
Major European Powers Involved
The major European powers involved in the French and Indian War were:
- Great Britain
- France
- Spain
- Austria
- Prussia
Great Britain and France were the main belligerents, with each side seeking to expand its empire in North America. Spain entered the war on the side of France, while Austria and Prussia fought on opposite sides.
Native American Tribes, French and indian war brainpop
Native American tribes played a significant role in the French and Indian War. They were allied with both the French and the British, and they fought on both sides of the conflict.
The Iroquois Confederacy was a powerful alliance of Native American tribes that sided with the British. The Iroquois Confederacy controlled a large territory in the Northeast, and they provided valuable support to the British in the war.
The French were allied with several Native American tribes, including the Huron, the Ottawa, and the Shawnee. These tribes provided the French with valuable support in the war, and they helped the French to maintain control of their territory in North America.
Causes of the War
The French and Indian War, a conflict that lasted from 1754 to 1763, was sparked by a complex interplay of factors, including territorial disputes, economic competition, and imperial ambitions.
Territorial Disputes
France and Great Britain had competing claims to vast territories in North America. France controlled the Mississippi Valley and the Great Lakes region, while Great Britain claimed the Atlantic coast and the Ohio Valley.
As settlers from both sides expanded their frontiers, they clashed over land and resources, leading to escalating tensions.
Economic Competition
Both France and Great Britain sought to control the fur trade, a lucrative industry that provided valuable pelts for European markets.
The French had established a network of trading posts throughout the interior, while the British sought to expand their own trading operations into these areas.
Imperial Ambitions
Beyond economic motives, both France and Great Britain were driven by imperial ambitions. They aimed to expand their colonial empires and secure strategic advantages.
For France, the war presented an opportunity to strengthen its position in North America and challenge British dominance.
For Great Britain, victory would secure its control over the Ohio Valley and establish its supremacy as the dominant power in the region.
Key Battles and Events
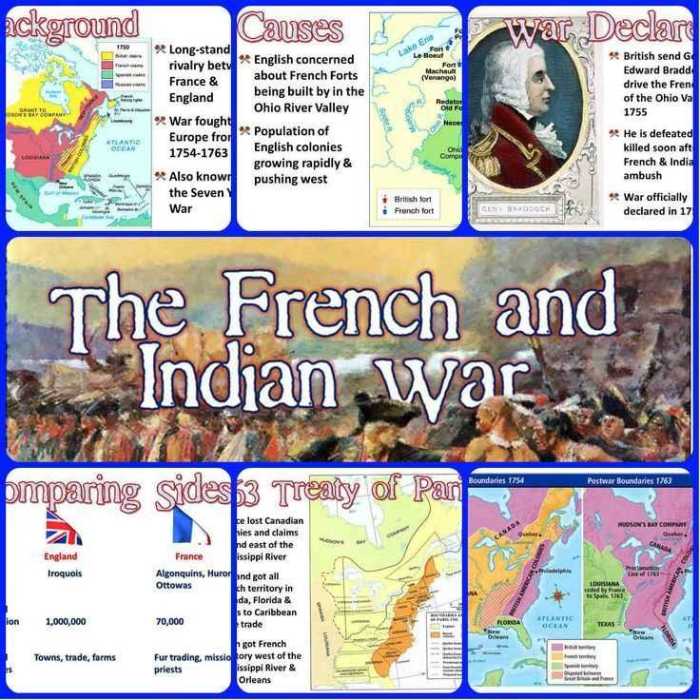
The French and Indian War unfolded as a series of significant battles and events, each shaping the course and outcome of the conflict. Both sides employed distinct strategies and tactics, with varying degrees of success.
Major Battles
-
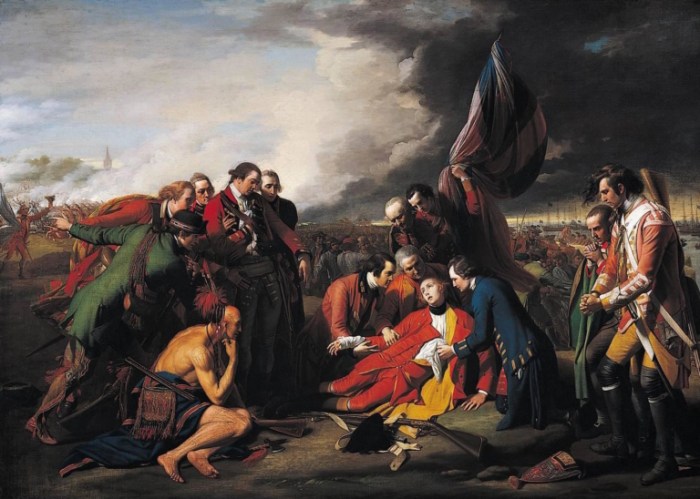
-*Braddock’s Defeat (1755)
A British force led by General Braddock was ambushed by French and Native American forces near Fort Duquesne, resulting in a decisive British defeat.
-*Capture of Fort William Henry (1757)
French forces under Montcalm captured Fort William Henry, a key British stronghold in New York, forcing the British to retreat.
-*Battle of Quebec (1759)
A pivotal battle in which British forces under General Wolfe scaled the cliffs of Quebec and defeated the French under Montcalm. Wolfe’s victory secured British control of Canada.
Just finished watching a vocab workshop on the French and Indian War, and it was super informative! I learned a ton about the causes and consequences of the war, as well as the major players involved. If you’re interested in learning more about this fascinating period in American history, I highly recommend checking out the video.
It’s packed with great information and insights.
-*Treaty of Paris (1763)
Ended the French and Indian War, granting Britain control of French territories in North America, including Canada and the Ohio Valley.
Strategies and Tactics
-
-*British
Focused on traditional European warfare, relying on massed infantry formations and artillery. However, they struggled to adapt to the guerilla tactics employed by Native American allies of the French.
-*French
Utilized guerilla warfare tactics, relying on surprise attacks, ambushes, and knowledge of the terrain. They also formed alliances with Native American tribes, who provided valuable support and intelligence.
Significance of Victories and Defeats
Key victories, such as the Battle of Quebec, shifted the balance of power in favor of the British. Conversely, defeats like Braddock’s Defeat exposed the weaknesses of British strategy and boosted French morale. These events ultimately contributed to the British triumph and the expansion of their empire in North America.
Impact on Native American Tribes

The French and Indian War had a devastating impact on Native American tribes. Caught between the warring European powers, Native Americans lost land, lives, and cultural identity. They also played a significant role in the war, forming alliances with both the French and British.
Loss of Land and Lives
The war resulted in the loss of vast territories for Native American tribes. The British gained control of much of the Ohio River Valley, displacing Native American tribes that had lived there for centuries. The French lost their North American empire, and their Native American allies were left vulnerable to British expansion.
The war also took a heavy toll on Native American lives. Thousands of warriors were killed in battle, and many more died from disease or starvation. The war disrupted traditional hunting and farming practices, leading to food shortages and epidemics.
Loss of Cultural Identity
The French and Indian War also had a profound impact on Native American cultural identity. The war disrupted traditional ways of life and forced Native Americans to adapt to the changing political and economic landscape. Many Native American tribes were forced to cede their lands and move to reservations, where they were subjected to government control and assimilation policies.
Native American Alliances
Native American tribes played a significant role in the French and Indian War. They formed alliances with both the French and British, and their support often tipped the balance of power in favor of one side or the other. Some tribes, such as the Iroquois Confederacy, remained neutral throughout the war, while others, such as the Delaware and Shawnee, fought on both sides at different times.
The Native American alliances were complex and fluid, and they often shifted depending on the changing circumstances of the war. However, one common factor that influenced Native American decision-making was the desire to protect their land and way of life.
Treaty of Paris (1763)

The Treaty of Paris, signed on February 10, 1763, marked the end of the French and Indian War. It had significant implications for the balance of power in North America and shaped the future of the United States.
Territorial Changes
- France ceded all of its territories east of the Mississippi River to Great Britain, except for the city of New Orleans and a small area around it.
- Spain ceded Florida to Great Britain in exchange for the return of Cuba, which had been captured by the British during the war.
- Great Britain gained control of all French and Spanish territories in North America east of the Mississippi River, except for New Orleans.
Impact on the Balance of Power
The Treaty of Paris shifted the balance of power in North America in favor of Great Britain. Great Britain now controlled a vast majority of the land east of the Mississippi River, giving it a dominant position in the region.
Significance for the Future of the United States
The Treaty of Paris had a profound impact on the future of the United States. By removing France from North America, it opened up the possibility for the American colonies to expand westward. The treaty also laid the foundation for the American Revolution, as the colonists grew increasingly frustrated with British rule.
FAQ Compilation
What were the primary causes of the French and Indian War?
Territorial disputes between France and Great Britain, economic competition, and imperial ambitions fueled the conflict.
How did the war impact Native American tribes?
The war devastated Native American tribes, leading to significant loss of land, lives, and cultural identity.
What were the key terms of the Treaty of Paris?
The treaty ended the war, granted Britain control of French territories in North America, and established the Mississippi River as the boundary between British and Spanish territories.